
views
Choosing a Capacitor

Understand the basic idea of a capacitor. The capacitor acts as a storage tank for electrical power. The amount of power that the capacitor can store is measured in Farads and the general rule of thumb is that you will need one Farad of capacitance for every one kilowatt (or 1,000 Watts) of power demand in your system.
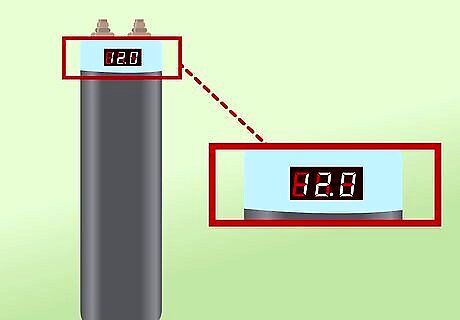
Decide whether or not you want an internal meter. Some capacitors come with built in meters that display their current charge. Keep in mind that if you go this route you will need to wire the meter into a switched power supply so that it the meter turns off with the car. Otherwise, the meter would stay on constantly and drain your system.

Purchase your capacitor. Odds are, if you need a capacitor, you have dropped some money on electrical components in your car. The cost of your capacitor could range from around $30.00 to over $200.00 depending on how large and how fancy you decide to go. Remember that they all serve essentially the same function, and that for most people a one Farad capacitor without an internal meter will work just fine.
Installing a Capacitor
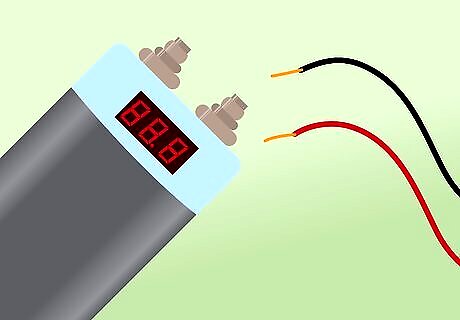
Be sure that your capacitor has been discharged. A charged capacitor can release a large amount of energy very quickly. This can be quite dangerous. You should always handle electrical components with care.
Disconnect the battery ground terminal. This will kill power electrical system and allow you to work safely. If you already have a capacitor in your system you will need to discharge it. Capacitors store power, and thus can still shock you even after removing the power supply.

Mount your capacitor.The capacitor can go in a number of places in your system. There is only a negligible difference in effectiveness no matter where you place it, but nearest the components that are struggling to get power (such as dimming headlights) is considered best. It is important that wherever you place it has a suitable place to mount the capacitor away from passengers. Although you are installing the capacitor to keep up with the extra power that is being pulled from accessories such as an upgraded stereo system, you have to remember that the capacitor is like a storage tank for power that supplements the whole system. By putting it close to the parts that are not getting sufficient power you allow it to supply power to those parts with minimal loss do to the extra resistance of a long wire.
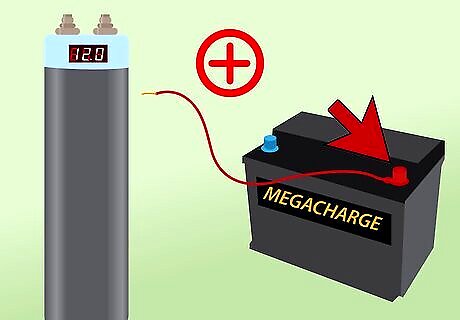
Connect the capacitor’s positive terminal. Whether you are connecting to the battery, amp, or a distribution block of some kind, you need to connect the positive terminal of the capacitor to the positive terminal of the other component by running a wire between them. Eight gauge wire is usually recommended.
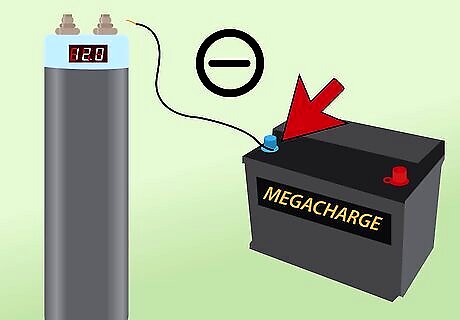
Connect the capacitor’s negative terminal. This terminal needs to be connected to ground.

Connect the remote turn on wire. If your capacitor has an internal meter, it will also have a third wire. This is the remote turn on wire and serves to kill power to the meter whenever the car is turned off. You will need to wire this into the remote turn on wire into any 12 volt switched power source (such as the ignition switch or amplifier).
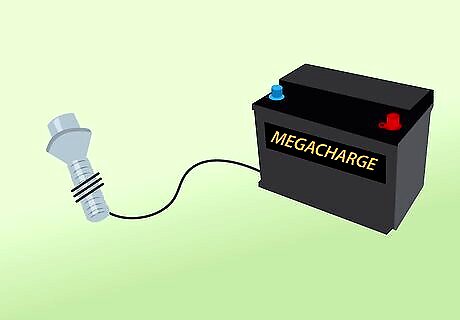
Reconnect the battery ground terminal. This will restore power to your system. All of your components should now be working.
Charging a Capacitor
Locate the main power fuse for your audio system. This fuse is installed with your system to prevent damage to the electrical components of your car, but will need to be removed before charging the capacitor. It should be near the battery on the main power line for your audio system.

Remove the main power fuse. This will provide you with a place to install the resistor that will help you charge your capacitor. The resistor allows the capacitor to charge more slowly. This prevents damage to the capacitor and the electrical system.
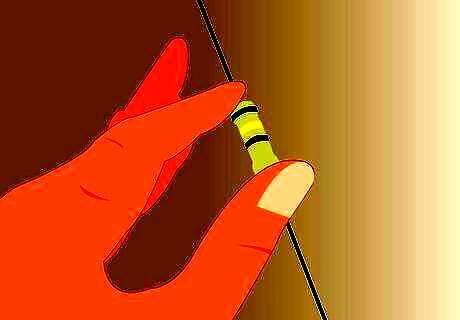
Put the resistor in place of the main power fuse. It is usually recommended to use a resistor that is 1 Watt and 500-1,000 Ohms. A higher impedance (Ohm value) will charge the capacitor more slowly and prevent damage. Connect the positive terminal of the capacitor to the resistor.
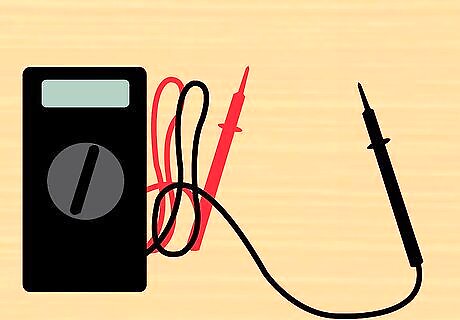
Measure the voltage on the capacitor with a voltmeter. A multi-meter will do the job fine as well. Set it to read DC Volts and put the positive lead of the meter on the positive terminal of the capacitor and the negative lead of the meter to ground. When the meter reads 11-12 volts, the capacitor is charged. Another way to charge a capacitor is to wire a test light from the positive terminal of the capacitor to the power line. As long as the capacitor is charging, there will be current flowing through the light and the light will shine. Once the capacitor is charged the light will go out because current will no longer be flowing (the voltage drop between the power line and the capacitor will be zero).
Remove the voltmeter. It is no longer necessary to monitor the status of the capacitor. If you used the light method, you can now remove the test light.
Remove the resistor. Disconnect the positive terminal of the capacitor from the resistor and disconnect the resistor from the power wire. It is no longer needed, so you can store it away in case you ever need to charge your capacitor again.

Replace the main power fuse. This will allow your audio system to receive power once again.



















Comments
0 comment