
views
- “He and I” is grammatically correct because “he” and “I” are both subject pronouns in the nominative case, which means they’re both doing the action in the sentence.
- “Him and I” is incorrect because “him” is an object pronoun and “I” is a subject pronoun. Instead, use “him and me” because “him” and “me” are object pronouns.
- Use subject pronouns when the people in the sentence are performing an action. Use objective pronouns when the people in the sentence are receiving an action.
Is it correct to say “he and I” or “him and I”?

“He and I” is grammatically correct. “He” and “I” are both subject pronouns, so this option is correct. “He and I” is a combined subject, which means that two subjects are joined together by a conjunction (“and”). You can tell if a sentence has matching pronouns by removing each of the pronouns or nouns and seeing if the sentence still makes sense. He and I went to the gym last week.He went to the gym last week.I went to the gym last week. Every day this week, John and I played pool at the bar.Every day this week, John played pool at the bar.Every day this week, I played pool at the bar.
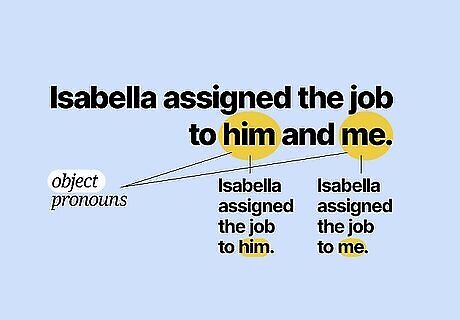
“Him and I” is grammatically incorrect, but you can use “him and me.” “Him” is an object pronoun and “I” is a subject pronoun, so they can’t be combined in a sentence. “He and me” is also incorrect. “Me” is an object pronoun, so you can say “him and me” instead. To see if a sentence has matching pronouns, remove each of the pronouns or nouns and see if the sentence still makes sense. Isabella assigned the job to him and me.Isabella assigned the job to him.Isabella assigned the job to me. My mother bought him and me new clothes for school, even though we didn’t want to go.My mother bought him new clothes for school, even though he didn’t want to go.My brother bought me new clothes for school, even though I didn’t want to go.
Subject Pronouns vs Object Pronouns
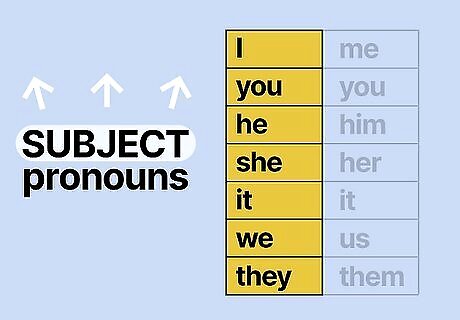
Use subject pronouns when the subjects perform an action. Subject or subjective pronouns tell you who or what the sentence is about. Use subjective pronouns like “I,” “you,” “he,” “she,” “it,” “we,” and “they” when the pronoun is the subject of (or the noun that does the action of) a verb. Sentences with singular subjective pronouns: He and I are going out for dinner. She and I found a turtle at the beach last week. You and it went on a walk around the block together. Jerry and I ate at the restaurant you told us about. Sentences with plural subjective pronouns: They learned that she’s going to the hospital instead. We traveled to the mountains after the vacation ended. A pronoun in the nominative case is the same as a subject or subjective pronoun.
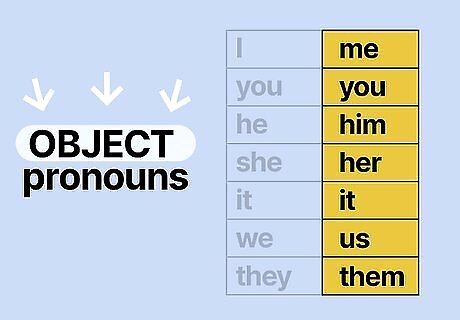
Use object pronouns when an action is done to the subjects. Object or objective pronouns receive the action described by the verb in the sentence. Use objective pronouns like “me,” “you,” “her,” “him,” “it,” “them,” and “us” when the pronoun is the object of (or the noun that’s receiving) a verb or preposition (like “around,” “in,” “to,” “by,” or “with”). Sentences with singular objective pronouns: On his run, Todd ran right by him and me. The house was too cold for her and it. The murder scene scared you and me. Paula spent the whole week with her and me. Sentences with plural objective pronouns: The cat followed them into the kitchen. The check was mailed to us (or him and me). A pronoun in the accusative case is the same as a direct object or objective pronoun.


















Comments
0 comment