
views
Whether you are looking to buy a new motorcycle or you are just a bike buff, learning about motorcycle engines and how they work is certainly refreshing. So here we bring you a quick guide into various types of engines mounted over most motorcycles.
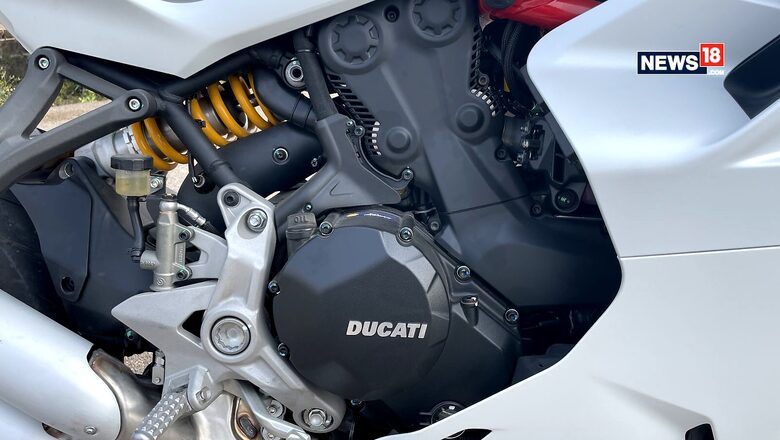
Motorcycle engines work in a four-step process known as intake-compression-power and exhaust. The first step is when the engine’s cylinder with a piston intake a mixture of fuel and air, next, it blocks the valves and compresses the fuel and then a spark plug creates an explosion that generates power which is ultimately transferred to the rear wheel, and then leftovers of the explosion are exhausted. Now, let us see how many kinds of engines are commonly used for achieving this task.
Single-cylinder: Cheap to produce and easy to maintain and fix, single-cylinder engines have one cylinder and piston doing all the work, which makes the engine more prone to vibrations.
Parallel-twin: Two cylinders are arranged side by side in this kind of engine and they work together to produce more power but at the same time, they consume more fuel. It is somewhat more balanced as the movement of one cylinder can cancel out the movement of the other, depending upon the firing order.
Inline-triple: This configuration uses three pistons, usually housed in the same cylinder block. Because the pistons are of odd numbers, the vibrations can not be cancelled, unlike an inline-four-cylinder.
Inline-four: Four parallel pistons housed in a single cylinder block, an inline-four engine is considered one of the smoothest engines running on a bike. The reason is its ability to balance pistons’ movement really well, thanks to the even number of engines. Almost all 600-1000cc sports bikes use this configuration.
Flat-twin or boxer: The configuration consists of two pistons horizontally opposed to each other. The advantage of this layout is that it keeps the bike's centre of gravity low and cylinders have a better chance to be air-cooled. This configuration, owing to its complicated structure, is expensive to build, maintain and fix.
Flat-four and flat-six: This configuration is similar to flat-twin except it has extra cylinders. These engines are capable of maintaining a great power delivery rate.
ALSO READ: Union Budget 2022: Special Mobility Zones for Electric Vehicles, New Battery Swapping Policy
V-twin: As you can guess from the name, the cylinders are aligned at an angle to each other forming a V-shape. While these engines require balancer shafts to cancel vibrations, they are known to produce a good amount of torque even at relatively low number revolutions. Bike makers may choose the angle between the pistons to specify the configuration further, such as making it an L-twin.
Also Watch:
V-4: More compact than inline-four, V-4 configuration is basically two V-twins brought together. They bring the bottom end torque delivery of V-twins along with the smoothness of inline-four. They need two-cylinder systems and hence are more expensive to manufacture.
Read all the Latest Auto News here

















Comments
0 comment