views
Trying Relaxation Techniques
Rest if your chest tightness is caused by soreness. Chest pain can be caused by a bruise or other injury. If that’s the case for you, take it easy. Stop doing any activity that might aggravate your injury. Once your chest pain gets better, you can start slowly getting back to your normal activity levels.

Get immediate stress relief. Panic attacks and other issues can cause trouble breathing and chest tightness. There are several techniques you can try to reduce acute stress, including: Yoga Relaxation techniques Breathing exercises

Work with a therapist to manage chest tightness caused by stress, anxiety, or depression. If you experience periodic chest tightness that doesn't have an obvious physical cause, ask your doctor to refer you to a therapist. Stress, anxiety, and depression can all cause feelings of tightness in the chest, even without becoming a full panic attack. A therapist may have you try: Cognitive Behavior Therapy (CBT) Talk therapy Relaxation techniques
Making Lifestyle Changes
Exercise to relieve chest pain accompanied by acid reflux. If your chest tightness comes along with heartburn, it is probably because of a gastrointestinal problem. Getting up and moving around, rather than lying down, can reduce this problem and the chest tightness it causes. Try some light exercise, like going for a walk or taking some stairs. You can also take antacids for quick relief from acid reflux.

Make dietary changes. Chest tightness caused by acid reflux can be alleviated by eating a modified diet, such as lowering your sodium intake. If your chest tightness is caused by heart problems, COPD, or other issues, your doctor may also make dietary recommendations, or suggest losing weight.

Talk with your doctor about additional lifestyle changes that may alleviate your chest tightness. Once your doctor figures out what's causing your chest tightness, they may recommend changing certain habits, like stopping smoking, to ease the problem. These may be used together with or instead of medication. Lifestyle changes that may reduce some types of chest tightness include: Exercising regularly Trying relaxation methods, like meditation Eating a well-balanced diet Avoiding caffeine, alcohol, tobacco, and drugs
Seeking Medical Care
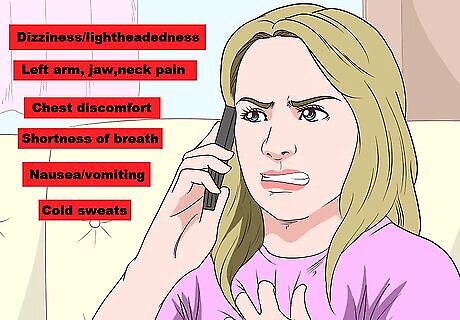
Get immediate medical attention for a heart event. A heart attack or other cardiac problem can cause chest tightness. Heart issues are serious, so contact emergency medical services immediately if you experience any warning signs. Do not try to drive yourself to the emergency room. Chew an aspirin and rest while you wait for help to arrive. Common signs of a heart event include: Chest discomfort Pain in the left arm, jaw, and neck Shortness of breath Nausea or vomiting Dizziness or lightheadedness Cold sweats
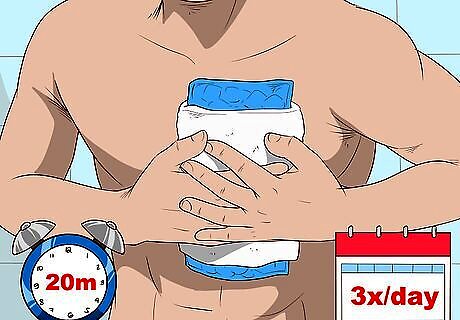
Apply an ice pack to swollen spots. An ice pack will help to reduce pain and swelling caused by injuries less than 6 months old. At the same time, it may ease the chest tightness the pain and swelling can cause. Apply the ice pack for 10 to 20 minutes at a time, 3 or more times a day. Place a towel between the ice pack and your skin. If the swelling goes down after a couple days but there is still pain/tightness, you can switch to a heating pad.
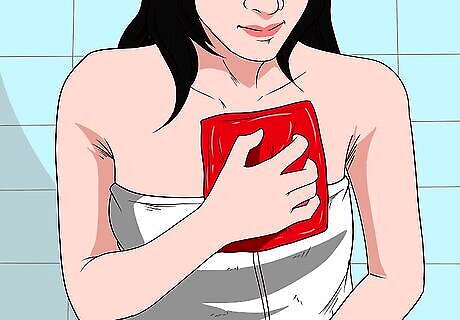
Place a heating pad on the sore area. Heat may be an effective way of relieving chest tightness due to old injuries. Place a thermal pad on the area of your chest that is impacted. If the pad is very warm, place a towel between it and your skin. You can use heating pads for relief as often as you'd like. If it is comfortable to recline, you can also try taking a warm bath for a similar effect.
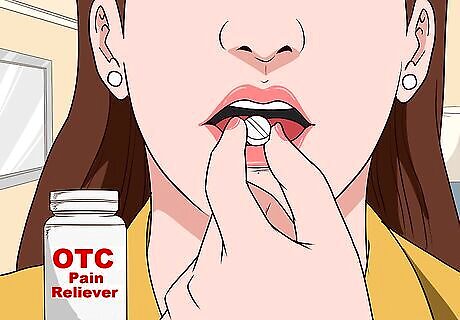
Take an over-the-counter (OTC) pain reliever. A dose of aspirin, acetaminophen (Tylenol) or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) like ibuprofen can give immediate relief from chest tightness. Follow the dosing guidelines on the package and don't take more than the recommended amount. OTC pain relievers are effective at treating chest tightness caused by muscle soreness or bone problems. If you are on any other medications, check with a doctor before taking an OTC pain reliever. They can advise you on which ones are safest and most effective.

Apply a muscle cream to aching areas. Ointments formulated to soothe sore muscles may ease chest tightness caused by this problem. Look for one with menthol. Rub the cream on the sore area, and follow the package directions to find out how often to use the cream. Once the muscle pain eases, the chest tightness should start to go away.
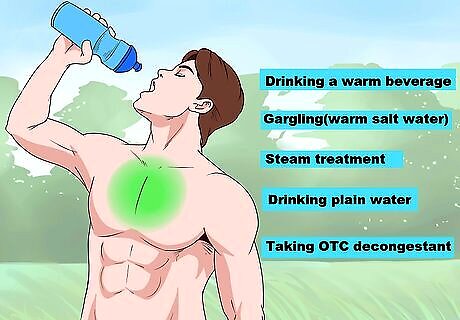
Clear chest congestion. If you have a cold or other issue that’s causing chest tightness, use an OTC or home remedy to break up the congestion. If you have frequent chest congestion, or if it lasts more than a couple days, you should contact a doctor. Quick remedies to help treat a cold and chest congestion include: Drinking a warm beverage (broth, lemon and honey tea, or ginger tea are good options) Gargling (stir half a spoonful of salt into a glass of warm water) Getting a steam treatment (such as taking a hot shower or bath), or using a cool mist humidifier Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of plain water Taking an OTC decongestant

Talk to your doctor about taking a Proton Pump Inhibitor (PPI). If you have frequent chest tightness accompanied by acid reflux or heartburn, you may have a chronic gastrointestinal problem. Let your doctor know, and they may prescribe a PPI. This type of medication will control the acid reflux and chest tightness that comes along with it. Alternatively, your doctor may prescribe an antidepressant. At low doses, some of them can have effects similar to a PPI’s. Your doctor may start you on a relatively high dose, then gradually decrease it over a period of a few months. It’s also possible that low acid production may cause you not to digest your food very well, in which case a digestive enzyme would be helpful. Talk to your doctor to get a complete diagnosis. A nutritionist can help you identify foods that are aggravating your symptoms.

















Comments
0 comment