
views
Common Causes and Fixes for Engine Knock

Insufficient octane fuel With rising gas prices, opting for the cheapest gas may be tempting. However, a fuel’s octane rating tells you how resistant fuel is to abnormal combustion. These ratings are listed alongside the regular, mid-grade, or premium fuel types. If you use a lower octane than the vehicle’s manufacturer recommended, fuel can pre-ignite, leading to an engine knock. The Fix: Refer to your vehicle’s owner’s manual for the required octane rating for your car. Most gasoline vehicles run on 87 octane. But double-check to keep your engine safe, especially for older vehicles.
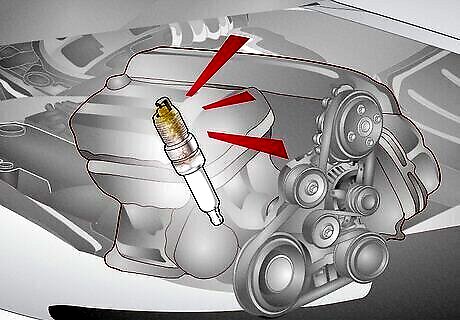
Faulty spark plugs Spark plugs produce a spark of electricity that helps the vehicle function. But, if a vehicle detonates or pre-ignites before the spark plugs can fire, it creates a knocking or pinging sound. This condition is also called a spark knock. The Fix: You’ll need to change your spark plugs by pulling the wire plug from the engine. Then, fit a socket wrench with an extension bar to slowly remove the spark plug from its housing. Swap the old spark plugs with the correct replacement plugs using the ratchet. DIY Cost: $16 to $100. Professional Cost: $100 to $500.

Excessive carbon deposits Each time the engine’s fuel fails to combust correctly, it leaves behind a build-up of carbon that looks like black soot. Over time, it can harden on the engine’s components, like the cylinder walls or spark plugs. This can disrupt the airflow, making the air-fuel ratio imbalanced. The Fix: While the fix is recommended for professional mechanics, you can purchase an intake valve and turbo cleaner. Warm and run the engine at 2,000 RPMs. Spray the product in short bursts through a vacuum line. Once the can is empty, accelerate the vehicle 2 to 3 times, avoiding going over 3,5000 RPMs. Run the engine idle for 1 minute, then turn the engine off. Reassemble the vacuum line and let the engine heat up for 1 hour. Shut the engine off and power the vehicle on again. Drive at highway speeds for 10 minutes. DIY Cost: $15 to $25. Professional Cost: $175 to $450.
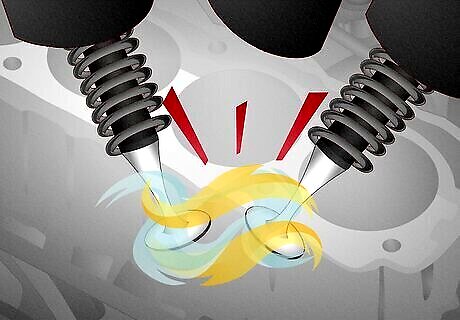
Incorrect air-fuel mixture Without the proper air-fuel mixture, the engine is susceptible to incomplete combustion and misfires, leaving you with a less fuel-efficient car that adds excessive pollution into the air. The Fix: One way to remedy the problem is by adjusting the air-fuel mixture screw. Allow the engine to warm up for 5 minutes, then locate the carburetor by the engine’s air filter. Look for a flat-headed brass screw and turn the screw clockwise with a flathead screwdriver. Listen for the engine’s idle sound and continue to adjust by turning in either direction until it sounds smooth. DIY Cost: $0 Professional Cost: $75.
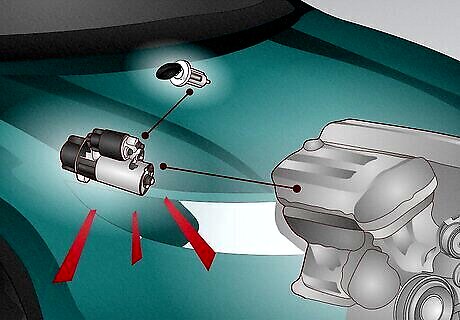
Poor ignition timing There are four key steps for an engine to run effectively: intake, compression, power, and exhaust. A vehicle’s ignition timing happens during the compression phase and controls when the spark plugs fire. However, if the timing is too early or too late, it can cause engine knocking or damage. The Fix: Ignition timing is controlled by the engine’s computer and can be a tedious DIY job. Professional Cost: $52 to $66.
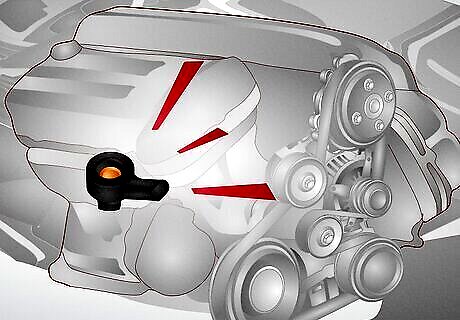
Bad knock sensor Nowadays, modern cars are equipped with knock sensors that automatically detect and prevent engine knocks by adjusting the ignition timing. However, if the knock sensor is faulty, you may not know there’s a problem with your engine until serious damage occurs. The Fix: A replacement is a tedious job. However, one way to do it is by unplugging the electrical plug from the bottom of the engine. Then, locate the knock sensor near the oil filter underneath the car. Remove the oil filter to access the knock sensor. Loosen the knock sensor with a wrench and fish and spin it by hand. Then, tighten it with a wrench and secure the plug to the engine. DIY Cost: $305 to $391. Professional Cost: $200 to $800.
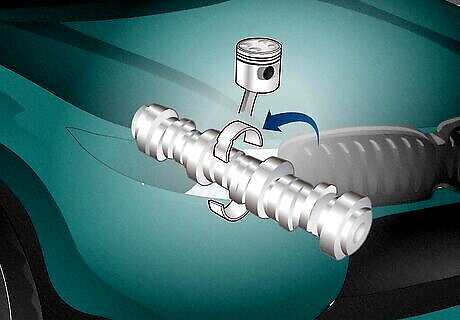
Worn bearings A vehicle’s pistons travel up and down the engine, turning the crankshaft to send power to the wheels. Rod bearings allow the piston to move smoothly, but over time, they can move or become worn out, which creates a rattling noise. The Fix: Replacing rod bearings is a difficult DIY job because they’re deep inside the engine. Refer to a trusted mechanic for assistance unless you have experience with car engines. You may need to have your engine rebuilt or replaced. Professional Cost: $2,000 to $3,000.
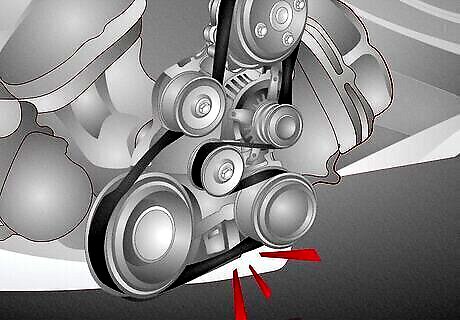
Bad belts or pulleys An engine relies on the performance of its timing belts and pulleys to run smoothly. However, where there’s strain on these components it can create a knocking or rattling sound. Similarly, the belts can come loose and knock against other components. The Fix: To replace a serpentine belt, take a wrench to relieve the tensioner and loosen the bolts. Pull the bolt and pulley out. Slip a replacement bearing into place and secure it with a bolt by hand. Thread a new belt through the pulleys. DIY Cost: $25 to $75. Professional Cost: $58 to $126.
Is an engine knock serious?
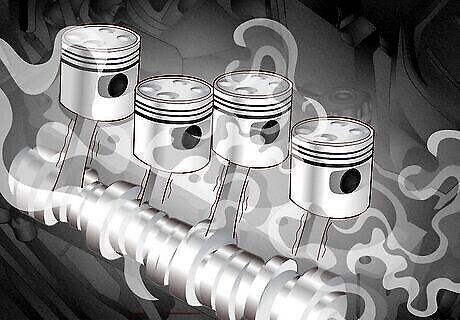
Yes—left unaddressed, an engine knock can cause severe damage. Any issue no matter how big or small, that has to do with the engine should be taken seriously. Excessive engine knocking can damage the piston, cylinder walls, and crankshaft bearings. Engine damage is one of the most expensive car repairs since it requires a complete rebuild or replacement. Depending on your vehicle’s make and model, replacing it can cost up to $10,000. If you’re wondering, can engine knocking cause permanent damage? The answer is yes, especially if the cause is worn rod bearings since these can cause the pistons to crash against the cylinder walls.
Can you drive with a knocking engine?
Limit your driving until you can have your engine diagnosed. If you hear a questionable sound from your engine, take your car to the nearest automotive shop for a quick diagnosis. Engine issues should be addressed promptly to limit damage. On average, diagnostic tests cost between $20 and $160.
Will an oil change fix a knocking engine?

Maybe—oil changes can help keep the engine lubricated. Adding or changing your vehicle’s oil may prevent your engine from knocking by providing sufficient lubrication to its components. It’s best to change your oil after every 3,000 miles. However, many modern lubricants can last 5,000 to 7,000 miles.
What is engine knocking?
Knocking happens when fuel burns unevenly in the engine. Engines consist of a fixed cylinder and a moving piston that supports spark ignition engines. When you start your ignition, fuel mixes with air into the cylinder. From there, the piston compresses this mixture while the spark ignites to power the vehicle. However, an imbalanced fuel-air mixture can cause a knocking sound. In many cases, engine knocks are heard during acceleration. So, you may not even realize it as you’re going about your day-to-day errands. For diesel engines, only air is pushed into the engine and compressed. Fuel is sprayed into the hot compressed air.


















Comments
0 comment