views
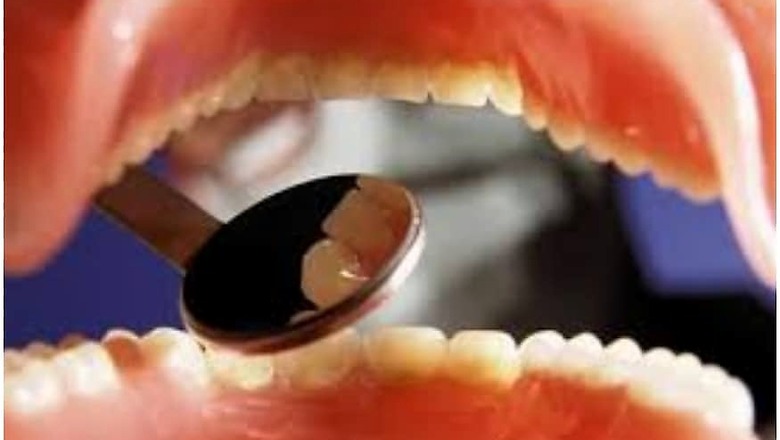
According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), World Health Organization (WHO) and Globocan 2018 survey, India accounts for one-third of all oral cancer cases in the world with nearly 2 lakh new cases registered every year. Oral cancer occurs in the tissues of the oral cavity or mouth (begins at the lips and extends backwards to the throat). The oral cavity comprises tongue, lips, gums and teeth, lining of cheeks (buccal mucosa), floor of the mouth and roof of the mouth (hard palate).
Warning signs
• Mouth sore or ulcer that does not heal even after proper treatment (most common presentation)
• Lump or thickening inside the mouth
• Whitish or red patch in the mouth
• Bleeding in the mouth
• Unexplained loosening of teeth
• Difficulty in wearing dentures (poor fit)
• Lump in the neck
Risk Factors
• Tobacco & betel nut/areca nut : All forms of tobacco, including cigarettes, beedi, pipes, cigars, and chewing (smokeless) tobacco
• Alcohol consumption: The risk for oral canceris about twice as high in people who have 3 to 4 alcoholic drinks per day compared to those who don’t drink alcohol. The risk is even higher in people who consume both alcohol and tobacco
• Sharp teeth or ill-fitting dentures: Chronic irritation of gums and cheek due to ill-fitting dentures or sharp teeth can increase risk
• Diet: Studies have shown that there is significant correlation between diet and oral cancer. It is advisable to consume diet rich in fruits and vegetables
• Weak immune system: People with weakened immunity are more prone to suffer from oral cancers. Certain immune deficiency diseases at birth, radiotherapy and chemotherapy, medicines given to organ transplant recipients and the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) may be responsible for this
• Exposure to ultra violet rays from the sun may cause lip cancer
Preventive measures
Oral cancer is preventable to a large extent as the risk factors like consumption of tobacco and excessive intake of alcohol can be controlled. One must refrain from chewing areca nut and betel nut. One must also consume plenty of fruits and vegetables.
Treatment
Treatment generally involves surgery. However, surgery cannot be classified as “standard” since each cancer is different and requires a personalized approach to treatment. The severity or stage of the cancer determines the extent of surgery (minor or extensive). The patient might require additional treatment either before or after the surgery such as radiotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted drug therapy, speech and swallowing therapy, physical and occupational therapies and pain management.
Reconstruction of the oral cavity post-surgery is another development in the treatment of this disease. The mouth performs many important functions such as speech, chewing, swallowing and surgery may compromise these. Microvascular free flap reconstruction and technology such as 3-D CAD CAM has revolutionized the result by providing a like-for-like replacement for what is removed.
(Dr Deepak Sarin is Director, Head and Neck Oncology, Cancer Institute, Medanta)
















Comments
0 comment