
118
views
views
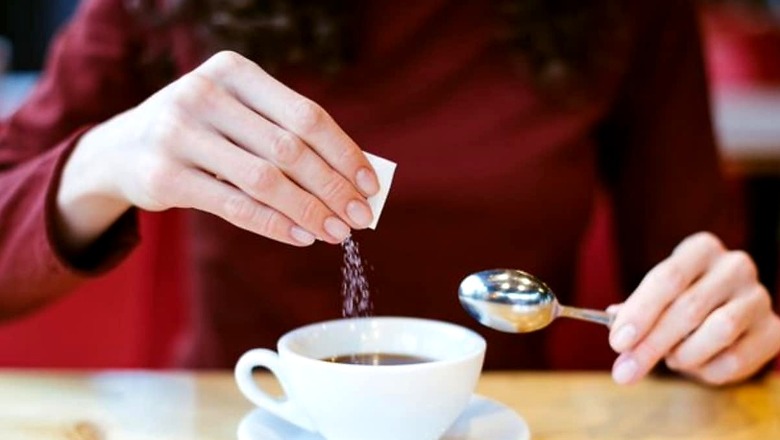
Sweeteners, often referred to as sugar substitutes or sugar replacers, are substances that impart a sweet taste to food and beverages
Sugar sweeteners, whether natural or artificial, entice our taste buds by mimicking the sweetness of sugar. They activate our sweet receptors, signaling pleasure to the brain. Natural sweeteners like honey provide additional nutrients, while artificial ones, like aspartame, offer zero calories. Understanding their mechanisms is key to healthier dietary choices and food industry innovations. Pranav Malhotra, Founder, Trunativ shares how sugar sweeteners work and the myths surrounding them.
How sweeteners work?
Sweeteners, often referred to as sugar substitutes or sugar replacers, are substances that impart a sweet taste to food and beverages. Many sweeteners come without any added calories and metabolic effects associated with sugar.
- Taste ReceptorsSweeteners activate taste receptors on our tongue, much like sugar does. However, majority of them do not provide calories because our bodies cannot fully digest and metabolize them.
- IntensitySweeteners are often many times sweeter than sugar, so only a small amount is needed to achieve the desired level of sweetness.
- MetabolismUnlike sugar, which is broken down into glucose and fructose in the body, some sweeteners are generally not metabolized, meaning they do not raise blood sugar levels.
Myths
- Sweeteners Cause CancerThis is a prevalent myth with no scientific basis. Extensive research has shown that approved sweeteners are safe for consumption when used within established guidelines, for instance Erythritol and Monk Fruit.
- Sweeteners Lead to Weight GainSweeteners themselves do not cause weight gain, in fact zero calorie sweeteners can be life changing. They can also be helpful in reducing calorie intake when used as part of a balanced diet.
- Sweeteners Are All the SameDifferent sweeteners have distinct taste profiles and properties. It’s essential to choose the right one for your specific needs and preferences. Ideally, going for zero calorie sweeteners with no bad aftertaste would work wonders.
Side Effects
- Digestive IssuesHigh consumption of sugar alcohols like sorbitol, mannitol, and xylitol can cause digestive discomfort, including gas and diarrhea, in sensitive individuals. Hence, being careful with your sweetener choices is advisable.
- Allergic ReactionsSome people may be allergic to specific sweeteners, resulting in symptoms like hives or itching.
- Bitter AftertasteCertain sweeteners may leave a bitter or metallic aftertaste for some individuals. However, there are great sugar replacers with no hint of bad aftertaste in the market like Trunativ’s Everyday Sweet.
Uses
- Sugar ReplacementThe most common use of sweeteners is as a sugar substitute in beverages, desserts, and baked goods.
- Low-Calorie and Sugar-Free ProductsThey are key ingredients in producing low-calorie and sugar-free versions of your favorite foods and drinks.
- Diabetic-Friendly OptionsSweeteners are a valuable tool for managing blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes.
- Weight ManagementThey can help reduce calorie intake and assist in weight management when used in place of sugar.


















Comments
0 comment