views
- Check your modem first to see if you need to buy a router or if there's one built into the modem you already have.
- First, connect the router to your modem and use a computer to log in to your router's admin page.
- Give your wireless network a name and password that others can use to connect to.
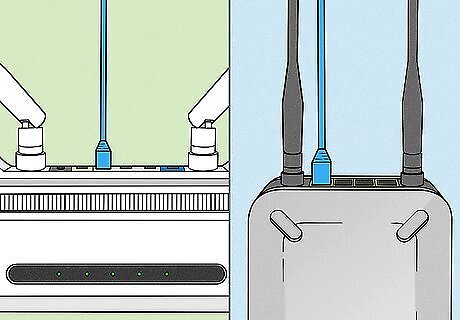
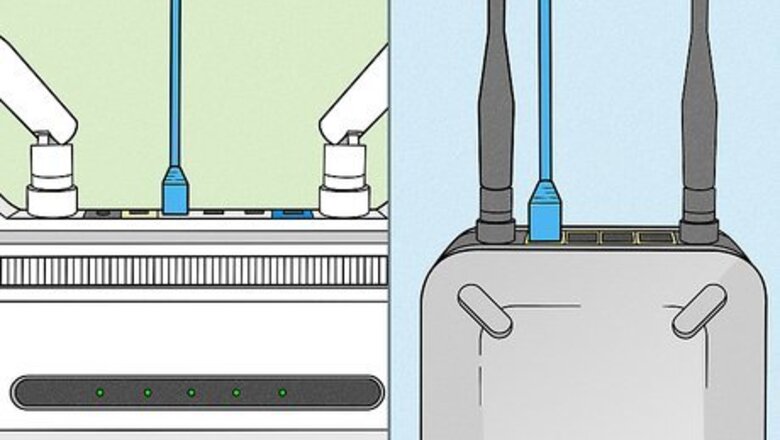
Connect your router to your modem. Routers and wireless routers enable you to share your broadband internet connection with multiple devices. If your internet provider didn't give you a router/modem combo device, you'll need to connect the router to the modem. For best results, place your router near your modem. Connect one end of an ethernet cable to the modem's LAN port, and the other end into your router's WAN port. Most routers come packaged with a short Ethernet cable that you can use for this. Routers come in all shapes and sizes, so make sure you get what you need by comparing features. If you have more area that you need to cover or have lots of walls in your home, you’ll need a router that offers the option of upgrading antenna(s) with high gain types - if not supplied in the box. If more than one wireless device will be connecting at the same time at different speeds, a MiMo-type router is recommended, otherwise, the speed for all devices will drop to the highest supported by all at that time.
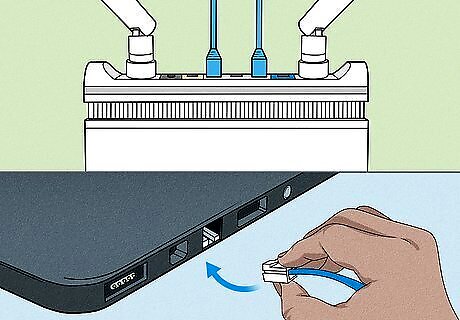
Connect the router to your computer with an ethernet cable. For the purpose of setup, you'll need to connect one end of an ethernet cable to your router's LAN port, and the other end to your computer's LAN/ethernet port. The router will assign a local or "private" IP address to any device connected to its LAN Ports or WiFi signal from a pool of private addresses (listed further below). WAN stands for "Wide Area Network" which is what the internet actually is. LAN stands for "Local Area Network". All modern routers should support 802.11n, or Wireless-N. This is the most stable, offers the fastest speeds, and is backward compatible with older standards such as 802.11g.
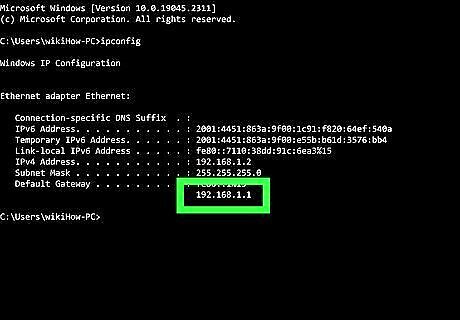
Find the IP address of the router. If this is a new installation or new router, find the default IP address that may be printed on a label on the router or in the documentation. If you can’t find the router’s IP address anywhere, you can do a web search for the router model to see what the default address is. IP addresses are formatted as four groups of up to three digits, separated by periods. Commonly found "default" Local IP addresses for routers are 192.168.0.1, 192.168.1.1, 192.168.2.1, and 10.0.0.1.
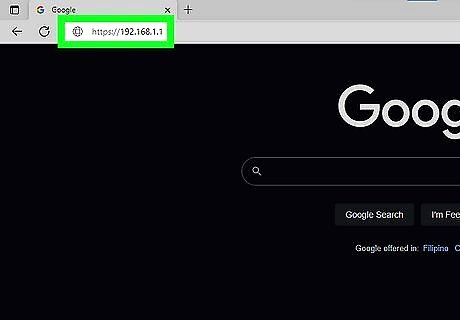
Open a web browser on a computer and go to your router's IP address. Enter in the IP address of the router into the address bar and press Enter. Your browser will attempt to connect to the router’s configuration menu. If you can’t figure out the correct IP address, username, or password, search for your router model online to see what the default login is. If it has been changed, press the Reset button on the back of the router for 10 (to 30+ seconds as dictated in the instructions for the router model) to restore factory defaults and try again.
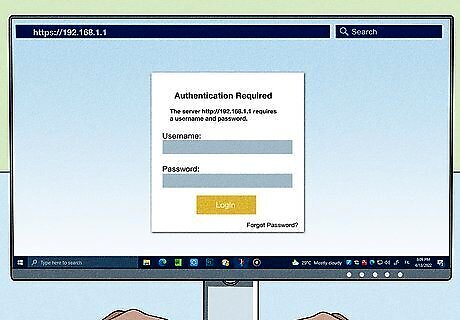
Enter your username and password. Most routers have a basic account set up that you will need to use to log on. This varies from model to model but should be printed on the router or in the documentation. The most typical username is “admin”. The most typical passwords are “admin” and “password”. Many routers will only require a username and a blank password, and some allow you to leave all fields blank.
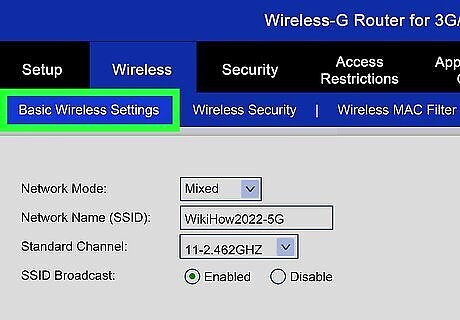
Open Wireless Settings. When you log in to your router, you will be taken to the router’s main menu or status screen, which may look different depending on your router's manufacturer. The "Internet" section can usually be left at default settings unless you received specific instructions from your internet service provider. The "Wireless" section will allow you to set up your wireless network, so navigate there.
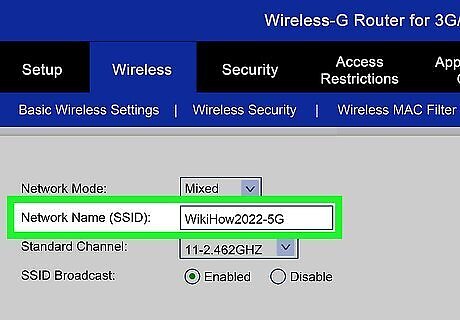
Enter a name for your wireless network. In the "Wireless" section, you should see a field labeled "SSID" or "Name." Enter a unique name for your wireless network. This is what other devices will see when scanning for networks. Check the box to enable SSID broadcast. This will essentially “turn on” the wireless network so that it may be readily seen by anyone in range of the signal. Leave this unchecked to make your network invisible. Only those who know your network name and password will be able to join.
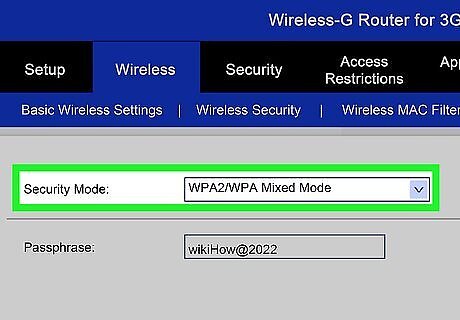
Choose a security method. Choose from the list of available security options. For the best security, choose WPA2-PSK as the encryption method. This is the most difficult security to crack and will give you the most protection from hackers and intruders.
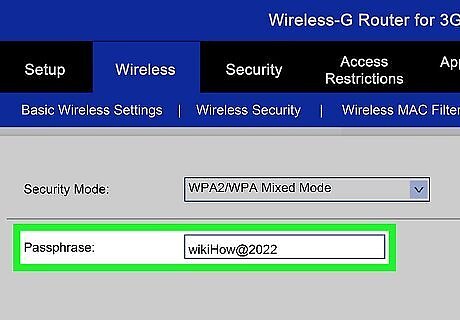
Create a passphrase. Once you’ve chosen your security method, enter a passphrase for the network. This should be a difficult password, with a combination of letters, numbers, and symbols. Don’t use any passwords that could be easily deduced from your network name or from knowing you.
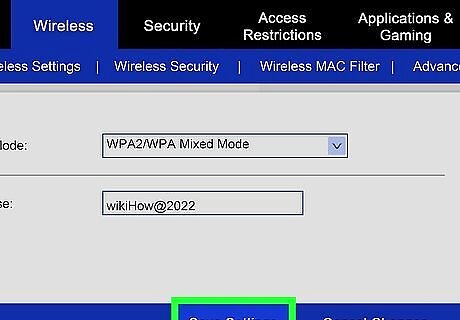
Save your settings. Once you are finished naming and securing your wireless network, click the Apply or Save button. The changes will be applied to your router, which may take a few moments. Once the router has finished resetting, your wireless network will be enabled. To connect to the wireless network on your phone, tablet, or computer, click your network and enter the password. You can also install a wireless printer so anyone on the network can use it. Connect a PlayStation 3 to a wireless network so you can access the online features. Connect an Xbox 360 to a wireless network so you can access the internet. Connect Apple TV to the wireless network so any network-related features are easier to use.
















Comments
0 comment