views
Setting Up Your Breeding Area

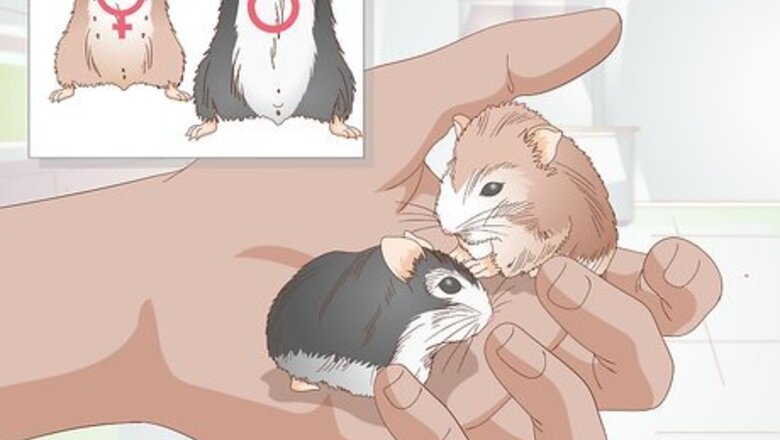
Pick out male and female dwarf hamsters. If you don’t already have a sexually mature male and female hamster, you should find one at the pet store. Check the genitalia to ensure that you are getting a male and a female. It is pretty tricky to tell the difference. For males, the testicles and anus are far apart. On females, the genitalia and anus are so close together they look like they are in the same place. You can find these points on the bottom of the hamster, just below the tail and between the hind legs. Make sure the males are at least 30 days old, and that females are at least three or four months old. It is better for the male to be older than 30 days, preferably around the same age as the female. Make sure they are healthy before purchasing so that you don’t have to worry about treating illnesses.
Set up cages for your hamsters. You need one cubic foot of space for a single dwarf hamster, and an extra half cubic foot per extra hamster in a cage. Size is very important for any hamster cage, but especially for breeding. The base should be solid, like a plank of wood or solid plastic. You need to have easy access to all parts of the cage. Consider getting a cage with tubes built in to give your hamsters a better quality of life. Just be prepared to break them down and scrub them out now and then. You do at least need a running wheel. Get bedding that is made from cellulose fiber or aspen wood shavings. Avoid cedar or pine shavings because the wood bears natural chemicals harmful for your hamsters’ lungs. Find a cage with extremely small openings or solid walls to keep babies from falling out of the cage. Place the mother’s cage in a quiet area after you have bred her. Give the female extra bedding for nest building material.

Supply hamsters with food and water. Attach a water bottle where the hamsters can easily reach. You can buy water bottles that hang on the side of a cage upside down. You can feed them with commercial hamster food available at the pet store. If you want to feed your dwarf hamsters fresh food, focus on seeds, whole grains, fresh green vegetables, and boiled eggs. After the mother gives birth, supply her with a slice of bread soaked in cow’s skim milk daily. Continue offering this milk bread until the pups reach four weeks. To minimize disturbing the mother after the pups are born, stock the feeder with food. You will be offering the milk-soaked bread, but if you stock the feeder well, you might not have to disturb the hamsters to refill it very much.
Handling Hamster Breeding

Wait until the female hamster is in heat. Sexually mature female hamsters are at least three or four months old. They go into heat (called estrus) every four days. Hamsters are nocturnal, so a female’s time of heat will occur at night and last for 12 hours. You will know your hamster has mated because her vagina will have a white substance in it. This is the “copulatory plug” and is proof that the male released sperm.

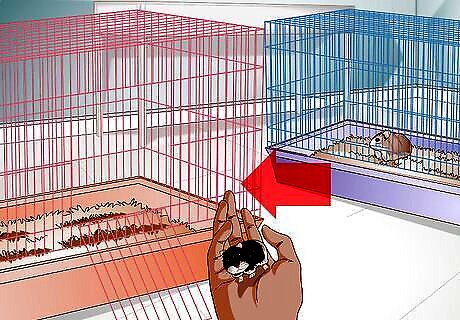
Place the hamsters together in one cage. When you see the female dwarf hamster in her estrus cycle, or in heat, you can place the male in the cage with her. Actually, since dwarf hamsters can live quite happily in the same cage, you might keep mating pairs together until the female gives birth. If you place the mating pair together without supervision, the female will become pregnant quickly. Evidence of a female’s first mating is blood near her genitalia, under the tail.

Watch signs of the female getting ready to deliver. She will build a nest late in her pregnancy by gathering bedding material into one location. She will also start to eat more, groom more, and dig more. She may become more restless and startle more easily.
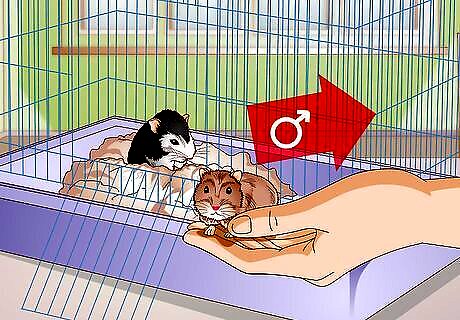
Remove the male before the birth. If the male is still present in the same cage with his family after the female gives birth, this puts the female’s life at risk. She will be in heat immediately after giving birth, and the male will mate with her. It isn’t healthy for her to get pregnant again right away. Take the male out when you see signs of the mother getting ready to give birth, such as nest building.
Taking Care of the Hamster Pups

Wait 18 to 30 days for the birth. Dwarf hamster gestation is between 18 and 30 days, but the average time from mating to birth is 21 days. The Roborovski hamster usually goes the full 30 days. Once you place a male and female together in a cage, you can expect to have pups within about three weeks. Remember to take the male out before the birth so that they don’t mate again right away. The female goes back into heat within 24 hours after having the pups.

Expect around 5 or 6 babies. The average size of a dwarf hamster litter is four to six pups. There can be as few as three and as many as twelve, however. They will nurse for about three weeks, although they will start to drink water at the two-week mark. They will huddle and move around the cage together. They will start to eat solid food at the end of their nursing days, anywhere between day 16 and 21.
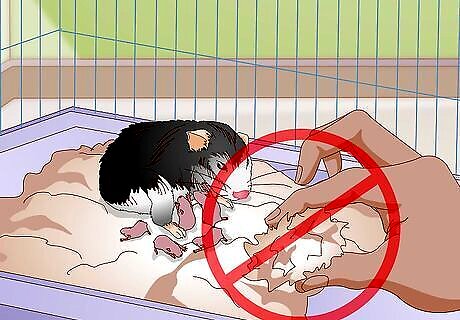
Avoid touching the nest after the birth. The mother hamster will be quite skittish while she nurses. For the first three weeks after the pups are born, avoid touching the nest at all costs. The mother might panic and kill her babies. If you need to clean an area of the cage, use something besides your bare hand to get it out. Be very careful to avoid the nest. A tissue can be used instead of your hand. Try to keep your human smell out of the cage. You might also consider fully stocking a water bottle and the food bowl so that you spend as little time as possible disturbing the mother hamster.

Separate the male babies after 4 weeks. You should remove male pups after they are weaned (at age four weeks). They are sexually mature at this age, and you want to prevent inbreeding. Dwarf hamsters are more mild than other breeds, so you can leave the female pups in the cage with their mother. Since the father will reject male babies, place the male pups in their own cage after they are weaned. Since they wean at about three weeks, giving them one extra week with their mother to adjust to life on solid food is good.
Watch the babies eat solid food. When the babies are about three weeks old, or between 16 and 21 days old, they will start to eat solid food on their own. Make sure you stock the cage's feeder with enough food for both the mother and babies.




















Comments
0 comment