views
- Ethanol and methanol are both types of alcohol. Ethanol is the kind found in alcoholic beverages, while methanol is toxic and used for industrial purposes.
- Both chemicals are clear, flammable, and smell like alcohol. Ethanol produces blue flames when it’s burned, and methanol burns white or nearly invisible.
- Ethanol is made through fermentation for drinkable alcohol or produced in factories for things like fuel. Methanol is made artificially to produce other chemicals.
Methanol vs. Ethanol: An Overview
Ethanol is the alcohol you drink and methanol is an industrial chemical. Both are clear liquids that smell like alcohol, but methanol is incredibly toxic and can cause severe nerve damage or death if consumed. Methanol is produced artificially to make things like insecticides, formaldehyde, and antifreeze, while ethanol can be made through fermentation for alcoholic beverages. Ethanol has industrial uses as well and can be found in motor fuel and lots of cosmetic products, like perfumes and lotions.
Chemical Differences
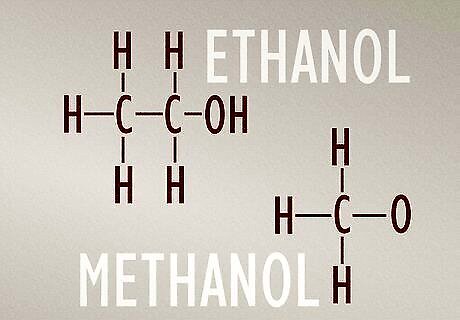
Ethanol molecules have 2 carbon atoms and methanol molecules have 1. Ethanol and methanol are both types of alcohol. Chemically, they consist of an ethyl group (C2H6) or methyl group (CH3) bonded to a hydroxyl group (–OH). Ethanol’s extra carbon atom is what makes these chemicals different from each other, even though they share some physical properties. The molecular structure of an ethanol molecule is C2H6O. The molecular structure of a methanol molecule is CH3O.
Physical Properties

Ethanol and methanol are both clear, colorless liquids. Visually, they’re indistinguishable from each other. This isn’t an issue in carefully controlled laboratory or industrial settings, but has proven to be dangerous when people attempt to make moonshine and accidentally create methanol (which is poisonous) instead of ethanol (which can be safely consumed in moderation in alcoholic beverages).
Ethanol and methanol both smell like alcohol, but methanol is milder. The two chemicals have a sharp, burning type of alcohol smell (imagine the worst sniff of cheap vodka or rubbing alcohol you’ve ever inhaled). However, methanol’s scent is a bit sweeter and more distinct than ethanol. The smell is not a good indicator of how concentrated the vapors of either liquid are. A diluted solution will smell nearly as strong as a more robust one.

Ethanol burns blue and methanol burns white. Both chemicals are highly volatile and flammable, but they burn differently because of their molecular structures. Ethanol burns a bright blue flame, while methanol burns bright white or nearly invisible.
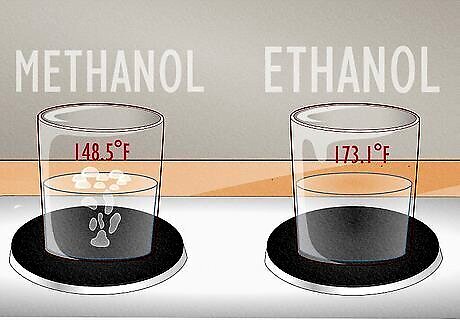
Methanol has a lower boiling point at sea level than ethanol. Pure methanol boils at 148.5 °F (64.7 °C) while ethanol boils at 173.1 °F (78.4 °C). This is because methanol’s molecular weight is lower than ethanol’s (this is why it evaporates faster, too).
Production

Ethanol is produced through fermentation, but can be synthesized, too. Humans began fermenting fruit juices to make alcoholic beverages in prehistoric times, and the process continues today. Simple alcohol fermentation occurs when fruit juices or grains (like corn, wheat, rye, or barely) are mixed with yeast or other bacteria to break natural sugars down into ethyl alcohol. Ethanol is known as “grain alcohol” because of these fermented grains. Today, ethanol is industrially synthesized en masse for fuel, cleaning products, and other solutions. Alcoholic beverages, like wine or vodka, are still made by fermenting fruit and grains with yeast (although the process is helped along by modern machinery). You can even ferment ethanol at home to make a DIY fuel (with the proper permits).
Methanol is almost exclusively synthesized in labs or factories. Historically, methanol was created when the cellulose in wood and some other plants fermented (it’s sometimes called “wood alcohol”). Since methanol is toxic and only used for industrial purposes, it’s now only made by a much faster, artificial process. Methanol is made by exposing carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen to a copper catalyst that forces them to combine into methanol molecules.
Effects on the Body

Ethanol is safe to drink in moderation and is what makes you feel drunk. When consumed in alcoholic beverages, ethanol causes slower reaction times, uncoordinated movements, slurred speech, and uninhibited feelings. Of course, over drinking can lead to blurred vision, confusion, and vomiting, or in severe cases, trouble breathing, a slowed heart rate, brain damage, or even death. You’re unlikely to encounter lethal doses of ethanol accidentally unless you work in a lab or chemical plant that mass produces it.

Methanol is highly toxic and should never be consumed. Besides drinking it, methanol can also be absorbed through your eyes, skin, or lungs if you inhale its fumes. The level of harm depends on the dose and duration of exposure. Mild exposure can lead to drunkenness, headaches, weakness, or loss of consciousness, while more severe amounts can lead to blindness or other nerve damage. Overexposure can cause death. You probably won’t encounter fatal doses of methanol unless you work in plastic manufacturing, vehicle deicing, or the fuel industry.
Industrial Uses

Ethanol is found in cosmetics, perfumes, fuels, and other materials. Outside of your favorite happy hour beverage, ethanol is used in a huge variety of products. It’s a common ingredient in colognes, lotions, mouthwash, and soaps, as well as less friendly compounds like dyes, inks, adhesives, preservatives, pesticides, plastics, and rubber. Ethanol is increasingly popular in fuels like gasoline. It’s technically a renewable resource since it’s made from biomass plant materials. Ethanol is also popular as an industrial solvent that can dissolve fats, oils, waxes, resins, and hydrocarbons.
Methanol is used in fuel, pharmaceuticals, and as an industrial solvent. It’s used to create harsh chemicals like insecticides, formaldehyde, acetic acid, chloromethanes, antifreeze, paint strippers, and spray paint, but is also found in helpful substances like antibiotics, vitamins, and hormones. You’ll never find it in an alcoholic beverage or any non-prescription product meant for consumption. Methanol can be added to petroleum to make fuel, though it’s no longer commercially available for this because of its somewhat nature. Pure methanol has no practical uses around the home and should only be stored in lab or factory settings.
How can you distinguish the difference?
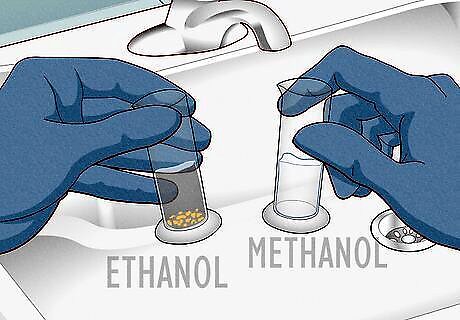
Perform an iodoform test to identify ethanol from methanol. Over a sink, add 10 drops of methanol and 10 drops of ethanol into separate test tubes. Then, add 25 drops of iodine and 10 drops of sodium hydroxide to each tube. Gently swirl each tube several times (the color of the iodine will start to fade). Check for an emerging difference in color after about 2 minutes. The ethanol tube will turn cloudy, and then a yellow substance called triiodomethane (iodoform) will form. The full formation takes about 20 minutes. The methanol tube will remain clear since it does not react to the iodine or sodium hydroxide. Wear gloves and goggles to stay safe during the experiment. Methanol and sodium hydroxide are dangerous if they get in your eyes or on your skin. Unless you’re a professional chemist, only perform this experiment under the supervision of an instructor.













Comments
0 comment