views
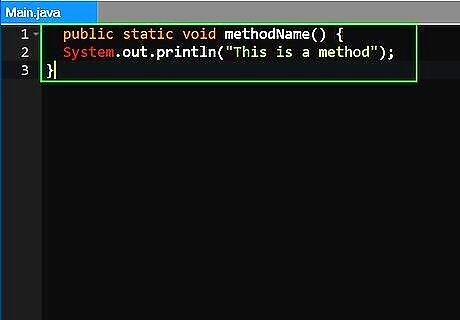
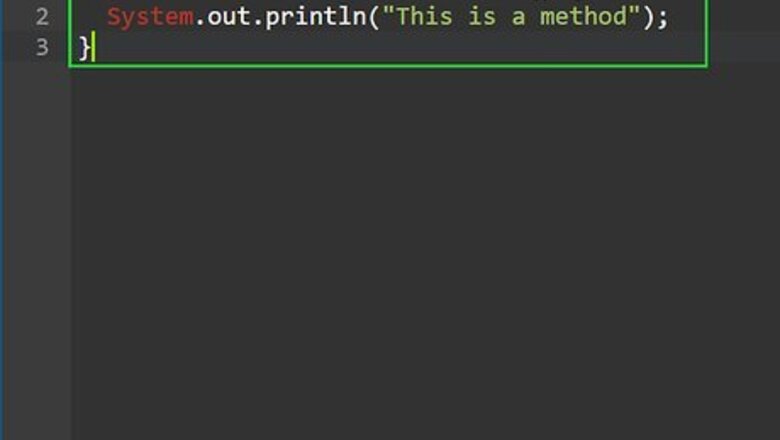
Understand what a method is. In Java, a method is a series of statements that create a function. Once a method is declared, it can be called at different parts of the code to execute the function. This is an useful way to reuse the same code over and over again. The following is an example of a simple method. public static void methodName() { System.out.println("This is a method"); }
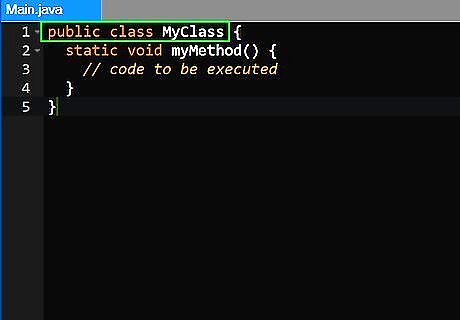
Declare the class access for the method. When declaring a method in Java, you need to declare what classes can access the method. In the example above, the access is declared as "Public". There are three access modifiers you can declare a method: Public: By placing the access modifier "public" before the method name allows the method to be called from anywhere. Protected: The "protected" access modifier, only allows the method to be called within it's class and subclasses. Private: If a method is declared private, then the method can only be called inside the class. This is called the default, or package-private. This means that only the classes in the same package can call the method.
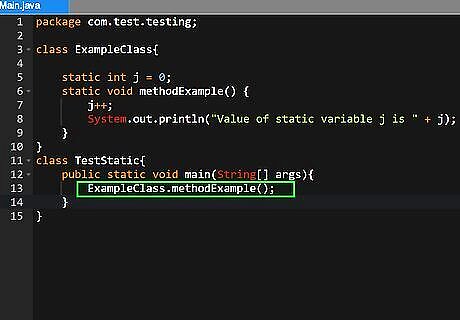
Declare the class the method belongs to. In the example above, the second keyword, "static" means that the method belongs to the class and not any instance of the class (object). Static methods must be called using the class name: "ExampleClass.methodExample()". If the keyword "static" was not used, then the method can be invoked only through an object. For instance, if the class was called "ExampleObject" and it had a constructor (for making objects), then we could make a new object by typing "ExampleObject obj = new ExampleObject();", and call the method with using the following: "obj.methodExample();".
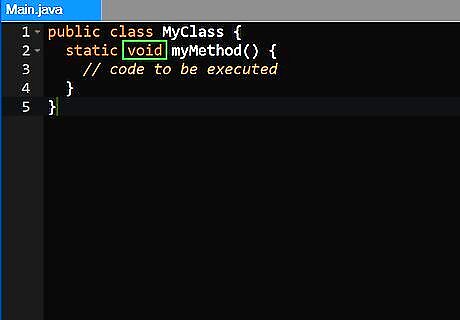
Declare the return value. The return value declares the name of the value the method returns. In the example above the word "void" means that the method doesn't return anything. If you do want a method to return something, then simply replace the word "void<" with a data type (primitive or reference type) of the object (or primitive type) that you wish to return. Primitive types include int, float, double, and more. Then just add "return" plus an object of that type somewhere toward the end of the method's code. When calling a method that returns something, you can use what it returns. For example, if a method called "someMethod()" returns an integer (a number), then you can set an integer to what it returns using the code: "int a = someMethod();"
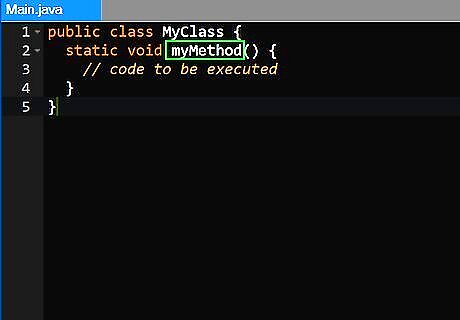
Declare the method name. After you've declared the classes that can access the method, the class it belongs to and the return value, you need to give the method a name so that it can be called. To give the method a name, simply type the method name followed by an open and closed parenthesis. The examples above include, "someMethod()" and "methodName()". You would then input all the method statements inside opened and closed curly brackets "{}"
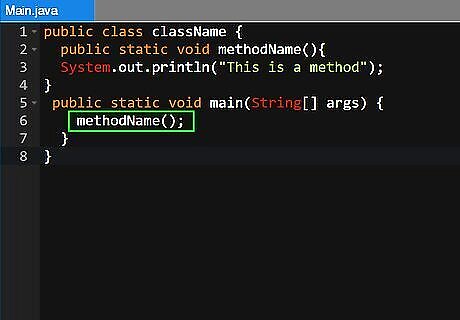
Call the method. To call a method, you just need to type the method name followed by open and closed parentheses on the line you want to execute the method. Make sure you only call a method within a class that has access to it. The following is an example of a method that is declared and then called within the class:. public class className { public static void methodName(){ System.out.println("This is a method"); } public static void main(String[] args) { methodName(); } }
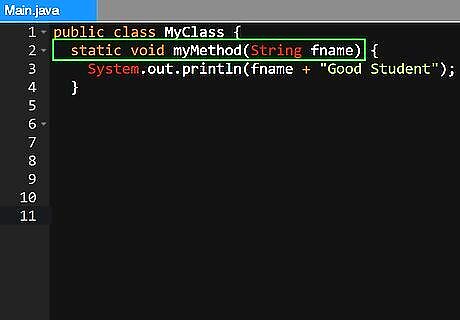
Add a parameter to a method (if needed). Some methods require a parameter such as an integer (a number) or a reference type (such as the name of an object). If a method requires a parameter, you just simply type the parameter in between the open and closed parenthesis after the method name. A method that requires an integer parameter of an integer would look like "someMethod(int a)" or similar. A method that has uses a reference type would look like "someMethod(Object obj)" or similar.
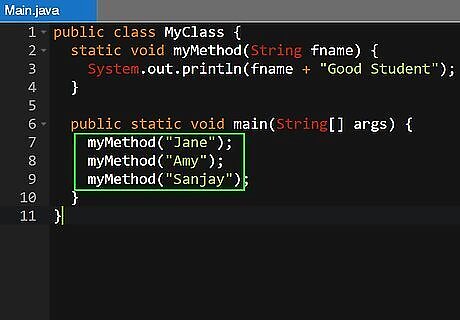
Call a method with a parameter. When calling a method that requires a parameter, you would just simply add the parameter in the parethesis after the method name. For example:"someMethod(5)" or "someMethod(n)" if "n" is an integer. If the method requires a reference object, simply enter the name of the object in the open and closed parenthesis. For example, "someMethod(4, thing)".
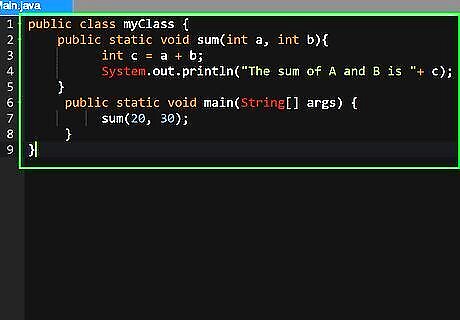
Add multiple parameters to a method. Methods can also have multiple parameters, simply separated by commas. In the following example, a method is created to add two integers together and return the sum as the return method. When the method is called, the two integers are given as parameters will be added together. When the program is run, you will receive an output that says "The sum of A and B is 50".: public class myClass { public static void sum(int a, int b){ int c = a + b; System.out.println("The sum of A and B is "+ c); } public static void main(String[] args) { sum(20, 30); } }

















Comments
0 comment