
views
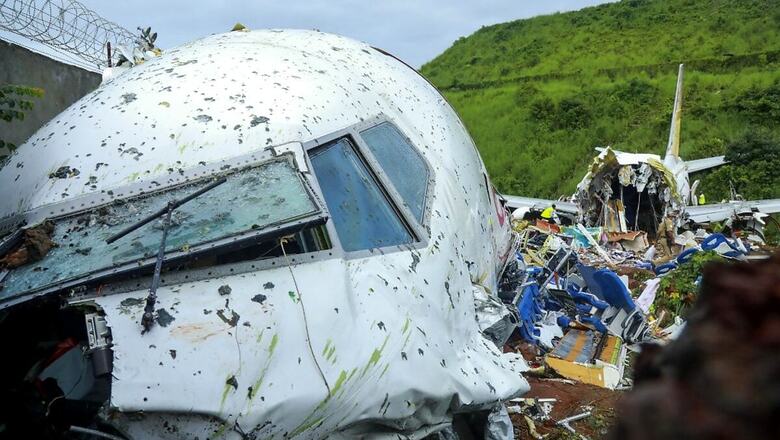
The black boxes from the Air India Express plane that crash-landed at the Karipur airport near Kozhikode on Friday evening, killing 18 people, have been recovered as a probe team landed in Kerala on Saturday.
A DGCA official said that the Digital Flight Data Recorder has been recovered from the aircraft, while the Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) was retrieved after the floorboard was cut of the plane that broke into two pieces after it skidded off a tabletop runway amid heavy rain.
The digital flight data recorder (DFDR) and the cockpit voice recorder (CVR) jointly make up the "black box" in an aircraft.
The recorders store crucial information about the plane's altitude, position and speed, as well as records of conversations between the pilots, and will be critical to understand what happened to flight IX-1344. Officials said they will be brought to Delhi for further investigation.
Investigating officials from Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA), Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB), top officials of Air India and Air India Express reached Kozhikode from New Delhi early on Saturday, said Air India Express.
The Air India Express flight from Dubai with 190 onboard overshot the tabletop runway at Kozhikode airport on Friday night while landing in heavy rain and fell into a valley 35 feet below and broke into two, killing at least 18 people.
The DFDR keeps a record of data from plane's systems like airspeed, altitude and fuel flow. A good quality DFDR can store up to 25 hours of flight data. The CVR keeps a recording of all the conversations taking place in a plane's cockpit. A good quality CVR can store up to two hours of voice data.
Once recovered after the aircraft crash, the black box gives ample flight data and voice recording to the investigators to find out what led to the accident.
"The DFDR and CVR, which have been recovered from the plane, will help in finding the cause of this accident," the DGCA official. These devices are with the AAIB and will be sent to Delhi for further investigation, according to the official.
A tabletop runway is located on top of a hill or a plateau with one or both the ends overlooking a gorge. The Kozhikode airport in Kerala has a table-top runway and is operated by the Airports Authority of India (AAI).
An AAI spokesperson said runway 28 of the airport was in use and in the first landing attempt, the pilot could not sight the runway and requested for runway 10.
Citing information from the Air Traffic Controller (ATC), the spokesperson said the aircraft touched down near taxiway 'C', which is approximately 1,000 metres from the beginning of runway 10. The total length of the runway is 2,700 metres. The spokesperson also said the reported visibility due to rains at the time of landing was 2,000 metres.
Aviation consultancy firm CAPA said on Twitter the DGCA and the AAIB must conduct thorough probes into the Kozhikode tragedy, and follow through on actions to achieve a systemic overhaul of aviation safety in India, especially at airports with tabletop runways.
The plane's pilot and the co-pilot were killed in the accident, K Gopalakrishnan, chief of the Malappuram district in Kerala, said. "All passengers have been admitted to various hospitals, and they are also being tested for COVID-19," Gopalakrishnan said, adding autopsy of the bodies would be carried out according to the COVID-19 protocol.
"Because of the weather conditions, he (the pilot) could not land the first time, so he did a turnaround and tried to approach it from a different direction," Civil Aviation Minister Hardeep Singh Puri told national broadcaster DD News, adding that only an investigation would reveal the cause of the crash.
He said it appears the crash was caused as the plane skidded off the runway. Tabletop runways are known for being difficult to land even for the best of the commercial pilots. It is essentially a runway built over a hill by levelling the surface. These high altitude runways have a steep drop either on one side or both sides.


















Comments
0 comment